
LEGAL AND ETHICAL CONCERNS OF TECHNOLOGY
Ownership and Licensing:
- Creations on a computer are owned by the creator or organization.
- Concerns arise with the easy access and distribution of digital content, emphasizing the need for protective measures. Licensing options include:
- Creative Commons, offering clear usage guidelines for intellectual property (IP).
- Open source, allowing free use, redistribution, and modification of programs.
- Open Access, enabling unrestricted access to online research.
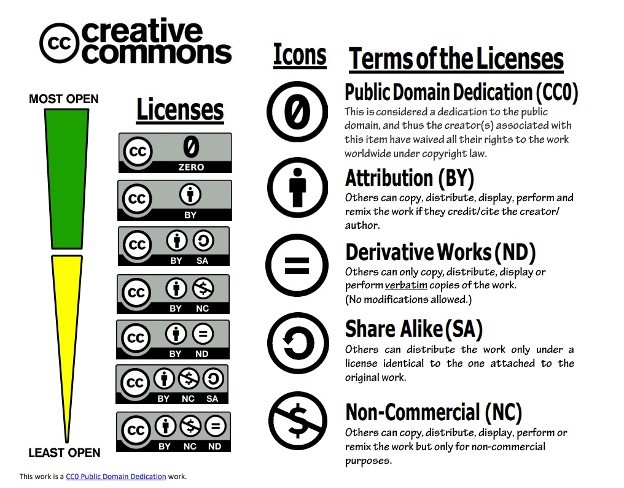
Ethical Use and Citation:
- Unauthorized use of someone else’s work is plagiarism, carrying legal consequences.
- Legal utilization involves seeking permission from the creator.
- Proper citation is essential when using material created by others.
Popcorn Hack #1
- Can you give an two different examples of how you might use citations in everyday life? (1 chocolate per answer, 3 answers total)
Broad Access to Digital Information:
- Creative Commons, open source, and open access contribute to widespread access to digital content.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Computing:
- Computing has legal and ethical considerations, especially in social and political contexts.
- The digital divide raises ethical concerns about unequal access to technology.
- Innovations like biased algorithms and data-collecting devices pose legal and ethical challenges.
Intellectual Property and Copyright Protection:
- Intellectual Property (IP) results from creative efforts and is protected by copyright.
- Copyright ensures exclusive usage rights, requiring permission for use.
![]()
Consequences of Violations:
- Plagiarism, presenting someone else’s work as your own, is against the law.
- Legal avenues for using others’ work include licenses such as Creative Commons, open source, and open access.
- People can face fines and prison sentences depending on the severity of the case.
Popcorn Hack #2
If a person copies and earns $2,500 from plagiarized work what legal repercussions could they face? Would they face fines or prison sentences, and for how long?
Copyright and Intellectual Property
Copyright is the legal right that the creator of a work has to it. The WIPO defines two types of rights under copyright:
Economic Rights: rights to financial benefits from the use of the work
Moral rights :rights that aren’t financial but are still important. For example, the right to claim authorship or the right to prevent harmful changes.
Copyright is not a new concept. Copyright laws have been around since the 18th century. However, the digital age has created new challenges to copyright and demands new ways to protect it as well.
Positives:
- Copyright gives the creator the right to prevent others from exploiting their work.
- Copyright promotes fair innovation. Copyright provides financial benefits to users.
Negatives of copyright:
- Copyright laws can get in the way of creative freedom as creators can get scared of building upon previous works because of copyright protection.
- Copyright only offers limited protection. For example, copyright protects a particular expression of an idea (as in images, words or sounds) but it does not protect the idea or concept itself.
Using content created by someone else without permission or citation can have consequences, such as a fine or an order to remove copyrighted content.
If you claim the said content was your own, even unintentionally, you might be found guilty of plagiarism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/copyright-4198743-01-FINAL-a21594dd0b6344f583f9ded410d8d6f8.jpg)
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is when you take the content of someone else and claim it as your own. The most common type of plagiarism students hear about is the plagiarism of written ideas and/or phrases. It’s possible to accidentally plagiarize by simply forgetting to cite the original source of an idea or phrase.
Plagiarism can have serious consequences, especially in the world of academia. It can get students expelled and see the careers of professors destroyed. Furthermore, there could be legal consequences as well.
It’s not difficult in the age of image searches and Turnitin.com to be caught plagiarizing or violating copyright. It can also be incredibly disheartening for content creators to see their hard work taken without permission or credit.
GPL and Black Duck:
-
In companies like Qualcomm, patents have been a way for the company to gain revenue. However, a term known as GPL(General public license) can create clashes with the legal rights of patents. GPL is known as the right for users to manipulate and use the software for their own benefits. GPL protects your rights with two steps: (1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it. An example is linux. Linux is open-source(original code which is made free and available for the public.) software, and users have the freedom to view, modify, and distribute the source code, provided they also distribute any modifications under the same GPL license terms. Open source licensing also contributed to helping both contributors and users and they are a binding legal contract between author and user that declares the certain conditions in which a piece of software can be used.
-
Back to qualcomm, GPL can prohibit people from making money off of their patents, which doesn’t favor the creators of the code. Qualcomm instead wants something known as royalty payment where the ones using the code, patent, or idea should pay royalty. Royalty payment is defined as a regular fee paid by a licensee to a licensor in exchange for the licensee to gain access to the licensors code.
-
Black Duck® software composition analysis (SCA) is a tool that helps development teams manage risks linked to open source and third-party code in applications and containers. It addresses security, quality, and license compliance concerns, ensuring software integrity by identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities while maintaining adherence to licensing requirements.
-
This whoel comcept may sound simple and unimportant, but think about the Students of Today, often they are given an assignment and instead of developing their own algorithm they opt to copy something off the internet. Well, don’t think the Workers of Today are entirely different. In summary, it is important to know the type of software license you are copying, it could impact billions of dollars in business.
GNU:
- GNU Stands for “GNU’s Not Unix,” an open-source operating system.
- It is rooted in software freedom, emphasizing users’ rights to run, study, modify, and share software.
- It includes the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) and essential libraries, forming the foundation for various software applications.
Android vs Apple Copyright Case
- Apple sued Samsung in 2011 for copyright infringements
- 7-year-long patent that resulted in a $1 billion ruling in Apple’s favor
- Involved with similarities between the Apple iPhone and Samsung’s Galaxy S line
- In 2014, the jury found in favor of Apple, awarding Apple almost $120 million for patent violations. However, the jury also found Apple also infringed Samsung’s patents, awarding $158,400
- In the end, Samsung faced heavy losses but was able to gain more market recognition and grow its business ventures.
- Helped set the precedent for patent and copyright cases
Redhat Legal Implications
Open Source Compliance:
- Crucial adherence to open-source licenses.
- Non-compliance may lead to legal actions and reputational damage.
Patent Litigation:
- Potential facing of patent infringement claims.
- Costly legal battles impacting product delivery.
- Claims involve unauthorized use of patented inventions, especially in software and open-source technologies.
Intellectual Property Protection:*
- Balancing intellectual property protection with open-source principles is crucial for Red Hat.
Data Privacy and Security:
- Strict compliance with data protection laws is essential.
- Breaches may result in legal consequences and regulatory penalties for Red Hat.
Homework
-
Describe the key differences between the Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal, Open Source MIT License, and Open Source GPL License. Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal (CC0): CC0 is designed to dedicate works to the public domain, allowing creators to relinquish all copyright and related rights. It offers maximum flexibility by removing restrictions on usage, modification, and distribution, imposing no conditions on users.
Open Source MIT License: The MIT License, a permissive license, enables developers to freely use, modify, and distribute software while requiring the inclusion of the original copyright and license notice. It is simple and permissive, with minimal restrictions.
Open Source GPL License: The GPL is a copyleft license aiming to keep derivative works open source. Users can freely use, modify, and distribute the software, but any distributed derivative work must adhere to the GPL, creating a “viral” effect.
- Give examples that illustrate how companies, such as Qualcomm and Red Hat, have leveraged Open Source licenses to establish unique business models.
- Qualcomm has embraced open source licenses for components in its products, contributing to the Android OS, fostering collaboration, and promoting Qualcomm’s hardware adoption. Red Hat’s business model centers around open source, providing enterprise support, services, and solutions for Linux. Revenue is generated through subscription-based services, support, and consultancy.
- Why are businesses that heavily rely on Open Source software still need to generate income and how they manage this within the constraints of Open Source licenses.
- Even with open source reliance, businesses need income for sustained growth and support. Qualcomm benefits from broader ecosystem collaboration, while Red Hat generates revenue by offering enterprise-level support, services, and consultancy, creating a sustainable business model within the constraints of open source licenses.
Extra Credit
Explain the significance of choosing an appropriate license for personal and team GitHub repositories, especially for the CPT project. How does this relate to the broader themes of legal and ethical concerns in computing?
